Total alkalinity ppm as caco 3.
Boiler water hardness is increased by.
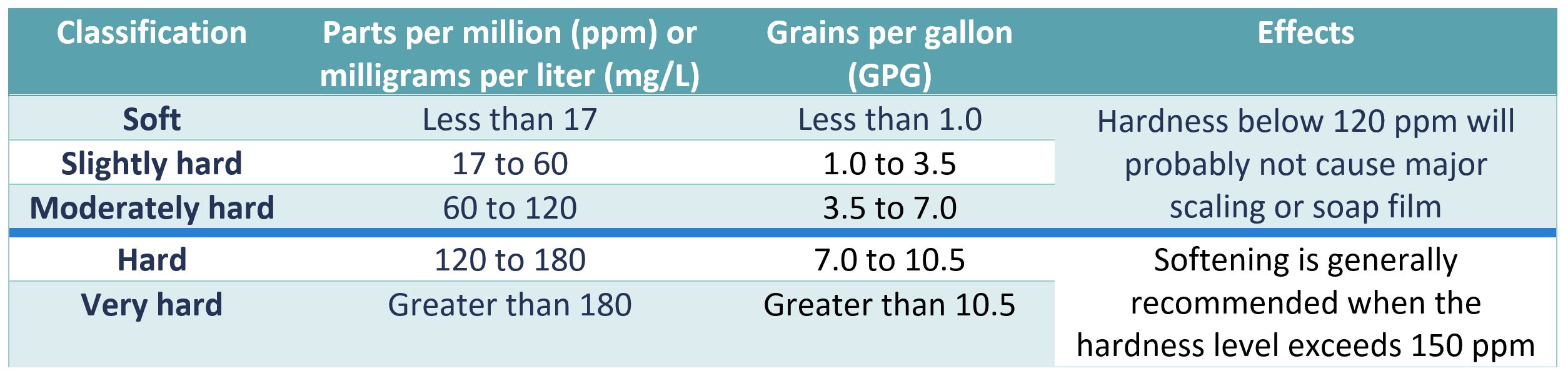
Today we are looking at how to conduct a water hardness test to check the water going to the boiler.
The chloride test is used often in conjunction with the conductivity test to regulate boiler blowdown.
This causes a lot of damage and increased maintenance.
If the impurities in the boiler feedwater are not dealt with properly carryover of boiler water into the steam system can occur.
These impurities leave deposits around the steam system.
Untreated water even water coming from a municipal water utility can contain dissolved salts which form scale on the heat transfer surfaces as the water is heated.
Contamination of the surfaces of control valves this will affect their operation and reduce their capacity.
Chelants have the ability to complex many cations hardness and heavy metals under boiler water conditions.
Therefore chlorides are used as a measure of boiler water concentrations i e.
How many times the mineral content which stays in the boiler when steam is produced of the raw water has been concentrated or built up in the boiler.
Hard water going into a steam boiler can lead to increased scaling and deposit build ups.
This may lead to problems elsewhere in the steam system such as.
They accomplish this by locking metals into a soluble organic ring structure.
The chelated cations do not deposit in the boiler.
The main disadvantage of this deposited.
Then boiler setpoints were reduced to increase the rate of solids removal and encourage increased soft water makeup into the boiler system until all traces of hardness were no longer entering the boiler feed water system.
It carries impurities such as dissolved solids with it.
These result from the precipitation in the boiler of feedwater hardness constituents due to heat and interaction of treatment chemicals and from corrosion products in the feedwater.
Silica ppm sio 2 lt.
Leading to increased carryover.